Autoimmune Diseases: Types, Causes & Treatment
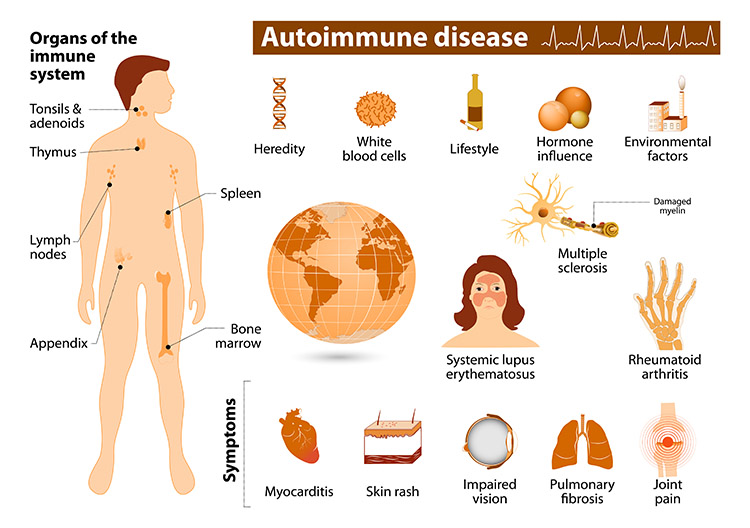
A disorder in which the body’s immune system fails to identify and targets its own healthy tissues as invading. Inflammation is a common symptom of autoimmune diseases, and it can affect many different regions of the body. The body parts affected differ based on the type of autoimmune condition a person suffers.
Fatigue, fever, muscular aches, joint pain and swelling, skin problems, gut pain, digestive problems, and swollen glands are all common indications and symptoms. Symptoms might be mild or severe, and they come and go. Autoimmune disorders come in many different types. Women are more likely to develop them, and they can run into families. Also known as an immune deficiency.
What are Autoimmune Diseases?
A disorder in which your immune system mistakenly targets your body is known as autoimmune disease.
Normally, the immune system protects us against pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. It sends out an army of fighter cells to attack these foreign invaders when it detects them.
Although, your immune system is able to distinguish between foreign invading and native cells.
The immune system misidentifies parts of your body, such as your joints or skin, as external in autoimmune disease. Autoantibodies are proteins released by the body that assault healthy cells.
Immune system disorders result in abnormally low or excessive immune system activity. Overactive immune systems cause the body to attack and destroy its own tissues (autoimmune diseases). Immune deficiency disorders reduce the body’s ability to fight against intruders, making it more susceptible to infection.
The immune system may produce antibodies that, instead of defending infections, attack the body’s own tissues in reaction to an unknown stimulation.
Types of Autoimmune diseases

There are over 80 various types of autoimmune diseases. They have the ability to affect practically every aspect of your body.
The following are some of the most frequent types of autoimmune diseases –
Joint and muscle diseases include:
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Gastrointestinal diseases include:
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Celiac Disease
- Crohn’s Disease
Skin oriented Diseases:
- Psoriasis
- Dermatomyositis
Nervous system diseases include:
- Inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a kind of chronic disease
- Guillain-Barre syndrome is a neurological disorder.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Other Chronic Conditions:
- Autoimmune Vasculitis
- Myasthenia Gravis
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Pernicious Anemia
- Vasculitis
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
What Are The Causes?
Causes of Autoimmune diseases depend upon a variety of factors that are unclear. However, there are several risk factors that can make you more likely to develop an autoimmune disease. The following are some of the risk factors:
- Some prescribed drugs. Consult your doctor about the potential adverse effects of blood pressure, statin, and antibiotic drugs.
- Having an autoimmune disease-prone family. Some disorders are hereditary, meaning they run in families.
- Smoking
- Just been diagnosed with one autoimmune condition. You have a good chance of getting another.
- When you are exposed to toxins
- Being a woman – women make up 78% of those with autoimmune diseases.
- Obesity
- Infections
How to Diagnose Them?
Most autoimmune diseases can’t be diagnosed with a single test. To diagnose you, your doctor will use a combination of tests, a discussion of your symptoms, and a physical examination.
When symptoms suggest an autoimmune disease, one of the first tests doctors employ is the antinuclear antibody test (ANA). A positive test indicates that you may have one of these diseases, but it does not specify which one or whether you have it for sure.
Other tests check for autoantibodies that are produced in autoimmune diseases. Non-specific tests may be performed by your doctor to check for the inflammation that these diseases cause in the body.
Symptoms of many autoimmune disorders are similar. Muscle aches, for example, are frequent in a wide range of disorders. As a result, getting a diagnosis of autoimmune diseases can take a long time and several visits to various types of doctors.
To assist your doctor in determining whether an autoimmune disease is causing your symptoms, do the following:
- Inform out about any health issues that your family had in the past. What diseases did your grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins suffer from? Make a list of everything you learn and share it with your doctor.
- Keep track of your symptoms, such as how long they continue and what causes them to improve or worsen. Give your doctor a copy of your notes.
- Consult a professional who specializes in the symptoms that are bothering you the most. If you get a rash, for example, you should see a dermatologist (skin doctor).
Sign and Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
An autoimmune disease’s symptoms vary depending on whatever region of your body is afflicted. The signs and symptoms of inflammation are redness, swelling, heat, and discomfort, which are common in autoimmune illnesses. However, the same symptoms can be caused by other disorders.
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can appear and disappear. During a flare-up, your symptoms may become more intense for a short period of time. You may experience a remission later on, which means that your symptoms improve or eliminate for a duration of time.
Many autoimmune diseases have similar early signs, for example:
- Fatigue
- Muscle ache
- Swelling and Redness
- Lowering Sustained Fever
- Hair loss
- Skin rashes
- Difficulty in concentration
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
Individual diseases can have their own set of symptoms. Type 1 diabetes, for example, produces excessive thirst, weight loss, and exhaustion. IBD is characterized by stomach pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
Treatment Options
Autoimmune disorders have no treatments, although their symptoms can be controlled. The immune system, genetics, and environment of each individual are all unique. This necessitates a one-of-a-kind approach.
The following are some examples of drugs used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases:
- Depression and anxiety medications
- Injections of insulin
- Medications for sleep
- Exchanges of plasma
- Corticosteroids
- Creams and tablets for eczema
- Immune globulin is given intravenously
- Anti-immunosuppressive drugs (also known as immunosuppressants) are medications that suppress (or pacify) your immune system
Complementary (alternative) medicines and ayurvedic treatments are used by some persons. Here are several examples:
- Herbs
- Acupuncture
- Chiropractic Procedures
Ayurvedic Treatment for Autoimmune Diseases includes:
Ayurveda is a holistic medicine that addresses the disease’s core cause. According to this, autoimmune disorders are caused by ama (toxic waste material), which is produced by low Agni (digestive fire) and low Ojas (spiritual fire) (immunity). Low Agni and weak Ojas are hence the core causes of autoimmune disease.
The Ayurvedic approach to autoimmune disease treatment focuses on restoring balance and boosting natural immunity. A tailored combination of remedies, medicines, foods, and lifestyle suggestions is also used to address the whole issue.
Read More – Role of Ayurveda in Cancer Treatment
Conclusion
Experts say “It’s going to require commitment, and it’s going to be difficult at times. However, learning to listen to your body and being aware of how your disease’s triggers is critical. It’s a decision you make for yourself.”